I believe that the "dust explosion" incident at Kunshan Zhongrong Metal Company in 2014 that shocked the whole country is still fresh in everyone's memory! This major liability accident caused 146 deaths and a direct economic loss of 351 million yuan. This explosion caused many families to lose their loved ones. This explosion caused this large company to go bankrupt in an instant. This explosion caused many related responsible persons to suffer. Legal punishment, painful price, and bloody lessons must be remembered. Let’s take a look at how the dust storm came about.
1 conditions for production
There are generally three conditions for dust explosions:
(1) Combustible dust is suspended in the air at an appropriate concentration, forming what is often referred to as a dust cloud;
All solid substances in a fine powder state are called dust. Dust that can burn and explode is called combustible dust; dust floating in the air is called suspended dust; dust that settles on solid walls is called deposited dust.
Explosive dust includes: metals (such as magnesium powder, aluminum powder); coal; grain (such as wheat, starch); feed (such as blood meal, fish meal); agricultural and sideline products (such as cotton, tobacco); forest products (such as paper powder, wood powder); synthetic materials (such as plastics, dyes).
The dust generated in the production process of some factories and mines, especially the dust generated in the processing of some organic substances, may cause explosion and combustion accidents under certain specific conditions.
(2) There is sufficient air and oxidant;
(3) There is a fire source or strong vibration and friction.
2 Explosion principle
Dusts that are generally more likely to cause explosion accidents include aluminum powder, zinc powder, ferrosilicon powder, magnesium powder, iron powder, aluminum processing grinding powder, various plastic powders, intermediates for organic synthetic drugs, wheat flour, sugar, sawdust, Dyes, bakelite ash, milk powder, tea powder, tobacco powder, coal dust, plant fiber dust, etc. The reason why the dust of these materials is prone to explosive combustion is that there are strong reducing agents such as H, C, N, S and other elements. When they coexist with peroxides and explosive dust, they will decompose and produce oxidation reaction. A large amount of gas, or a small amount of gas, releases a large amount of combustion heat. For example, aluminum powder has a risk of explosion as long as it is in a carbon dioxide atmosphere.
The difficulty of dust explosion is related to the physical and chemical properties of dust and environmental conditions. It is generally believed that substances with greater combustion heat are more likely to explode, such as coal dust, carbon, sulfur, etc. Substances that oxidize quickly are prone to explosion, such as magnesium powder, aluminum powder, ferrous oxide, dyes, etc. Dust that is easily charged can also easily cause explosions, such as synthetic resin powder, fiber dust, starch, etc. These poorly conductive substances accumulate static electricity due to friction with machines or air. When reaching a certain amount, they will discharge and generate sparks, forming a fire source for explosions.
Dusts that are usually less likely to cause explosions include soil, sand, iron oxide, abrasive materials, cement, quartz dust and dust similar to combustion. The dust chemical properties of this type of material are relatively stable, so they are not easy to burn. However, if this type of dust is produced in oil mist and flammable gases such as CO, CH4, and gas, it is also prone to explosion.
The explosion of dust can be regarded as developing from the following three steps: the first step is that the suspended dust is rapidly carbonized or vaporized under the action of a heat source to produce flammable gas; the second step is that the flammable gas is mixed with air and burned; The third step is that the heat released by the combustion of the dust is transferred to the nearby suspended or blown dust through heat conduction and flame radiation. After the dust is heated and vaporized, the combustion cycle continues. As each cycle proceeds, the reaction speed gradually accelerates, through violent combustion, and finally an explosion. This explosion reaction, explosion flame speed, explosion wave speed, explosion pressure, etc. will continue to accelerate and increase, and develop in leaps and bounds.
3 Characteristic hazards
3.1 Influencing factors
Physical and chemical properties
The greater the combustion heat of a substance, the greater the explosion risk of its dust, such as coal, carbon, sulfur dust, etc.; the more easily oxidized substances are, the more likely their dust is to explode, such as magnesium, ferrous oxide, dyes, etc.; The more electrically charged the dust, the more likely it is to explode. During the production process, dust generates static electricity that is difficult to dissipate due to mutual collision and friction, causing static electricity to accumulate. When it reaches a certain value, electrostatic discharge occurs. Static discharge sparks can cause fires and explosions. Dust explosions are also related to the volatiles they contain. For example, when the volatile matter in pulverized coal is less than 10%, explosion will no longer occur, so coke dust has no explosion risk.
The size of granule
The surface of dust adsorbs oxygen in the air. The finer the particles, the more oxygen is adsorbed, making it easier to explode. Moreover, the lower the ignition point, the lower the lower explosion limit. As the diameter of dust particles decreases, not only does the chemical activity increase, but it is also easily charged with static electricity.
Dust concentration
Similar to combustible gases, dust explosions also have a certain concentration range and upper and lower limits. However, most of the general information only lists the lower explosion limit of dust because the upper explosion limit of dust is higher.
3.2 Explosion characteristics
(1) Multiple explosions are the biggest feature of dust explosions.
The air wave of the first explosion will blow up the dust deposited on the equipment or the ground. A negative pressure will be formed in the center of the explosion within a short time after the explosion. The surrounding fresh air will fill in from the outside inward and mix with the raised air. The dust mixes, causing a secondary explosion. In a secondary explosion, the dust concentration will be higher.
(2) The minimum ignition energy required for dust explosion is relatively high, generally above tens of millijoules.
(3) Compared with flammable gas explosions, the pressure of dust explosions rises slowly, the higher pressure lasts for a longer time, the energy released is large, and the destructive power is strong.
3.3 Main hazards
(1) Extremely destructive. Dust explosions involve a wide range of industries, including coal, chemical industry, pharmaceutical processing, wood processing, grain and feed processing and other sectors.
(2) It is easy to produce a secondary explosion. The first explosion air wave blows up the dust deposited on the equipment or the ground. In a short time after the explosion, a negative pressure will be formed in the center of the explosion, and the surrounding fresh air will fill in from the outside inward, forming a so-called "return" Wind,” mixed with the blown dust, causing a second explosion ignited by the remnants of the first explosion. In the secondary explosion, the dust concentration is generally much higher than that in the primary explosion, so the power of the secondary explosion is much greater than that of the first explosion. For example, in a sulfur powder plant, an explosion occurred inside the grinder. The explosion wave spread from the grinder to the cyclone separator along the gas pipeline. A secondary explosion occurred in the cyclone separator. The explosion wave was generated on the cyclone separator after passing through the explosion. The crack spread into the workshop, raising sulfur dust that settled on buildings and process equipment, and another explosion occurred.
(3) Can produce toxic gases. One is carbon monoxide; the other is toxic gases caused by the decomposition of explosives (such as plastics) themse
4 Preventive measures
If effective ventilation measures are taken, smoking and working with open flames are strictly prohibited. Install pressure relief valves or other devices on the equipment shell, and use explosion containment systems. Factory buildings with the risk of dust explosion must be designed in strict accordance with the explosion-proof technical level, and separate ventilation and dust exhaust systems must be installed. Workshop floors and equipment should be wet-cleaned frequently to prevent dust from flying and gathering. Ensure that the system has good airtightness. If necessary, fill the combustible dust in the closed container or pipe with nitrogen, carbon dioxide and other gases to reduce the oxygen content and suppress the explosion of dust.
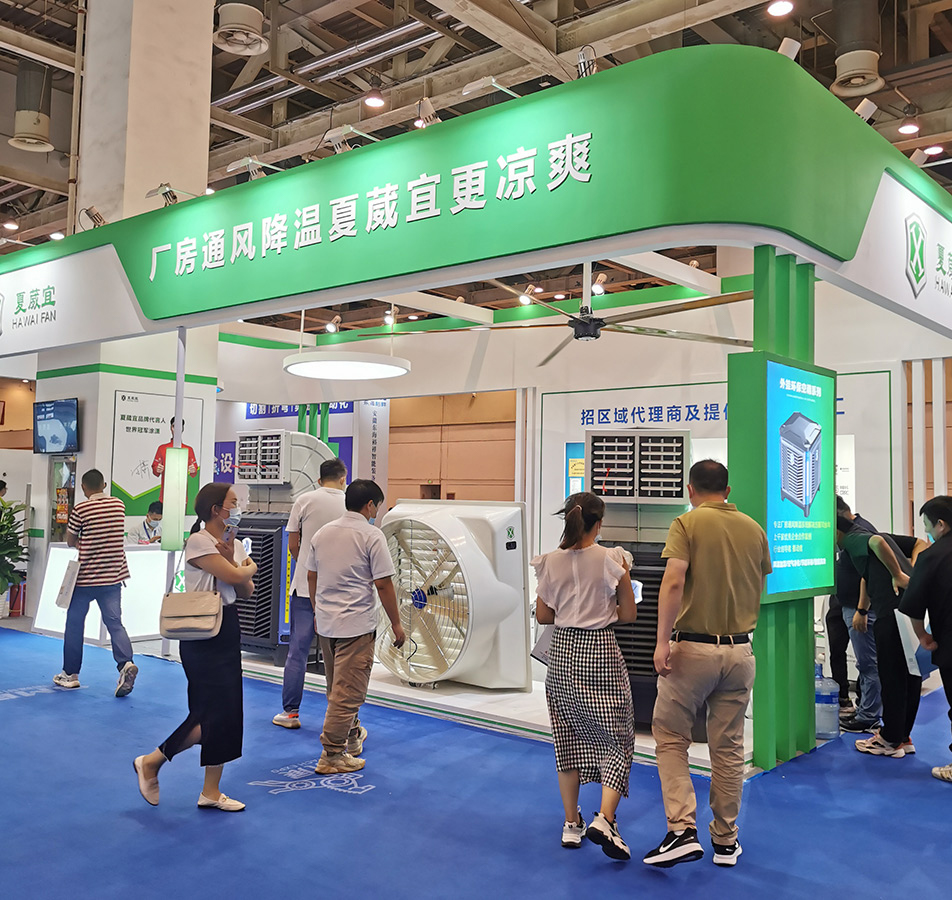
The Xiavii fan uses the ventilation and cooling principles of air convection and negative pressure ventilation to quickly discharge indoor bad smells (odor, heat, smoke, dust, etc.) to the outside, thereby making the indoor pressure lower than the outdoor pressure. At the same time, under the influence of atmospheric pressure Under the condition, fresh outdoor air will quickly flow into the room from the opposite window where the negative pressure exhaust fan is installed, and the air exchange rate can reach 60 times per hour (100M2 factory building), thus creating a natural and comfortable working environment with fresh air. In some places where combustible dust is generated in metallurgy, coal, chemical industry, electroplating, polishing, food processing and other industries, dust-filled environments often occur. Therefore, choosing better ventilation equipment will improve the environment of equipment and workshops and ensure production Safe operation is of great significance. The ventilation and cooling equipment produced by our company - negative pressure fan, can sweep away the dust, smoke and odor in your workshop! Negative pressure fans fully embody the five major advantages of high efficiency, energy saving, environmental protection, low cost of use, and wide range. They have become the ventilation brand of choice for many enterprises.











 Home
Home Products
Products Telephone
Telephone Message
Message






